By Jo Nova

Betelgeuse is the red giant at the top of Orion. Image by yoshitaka2 from Pixabay
Astronomers are very excited. A new paper suggests Betelgeuse — the red giant in Orion — might be only a decade or two (or maybe a century) away from going supernova. It’s the sort of thing that only happens once in a thousand years. Whenever it does go boom, it will shine brighter than the moon, and dominate the sky for a few months to a year.
It’s 600 light years away, so if it is going to go supernova in the next twenty years, then, of course, it must have already happened and the light is on the way.
Before anyone cracks the champers, the new paper by Saio is based on models trying to figure out what’s happening on a pulsating ball of fire 5,600 trillion kilometers away.
Will We See a Supernova in Our Lifetimes?
There hasn’t been a supernova in our neighborhood since July 4, 1054, when Chinese astronomers observed a supernova, now labeled SN1054, that remained visible for almost two years. The remnants of that supernova are now called the Crab Nebula.
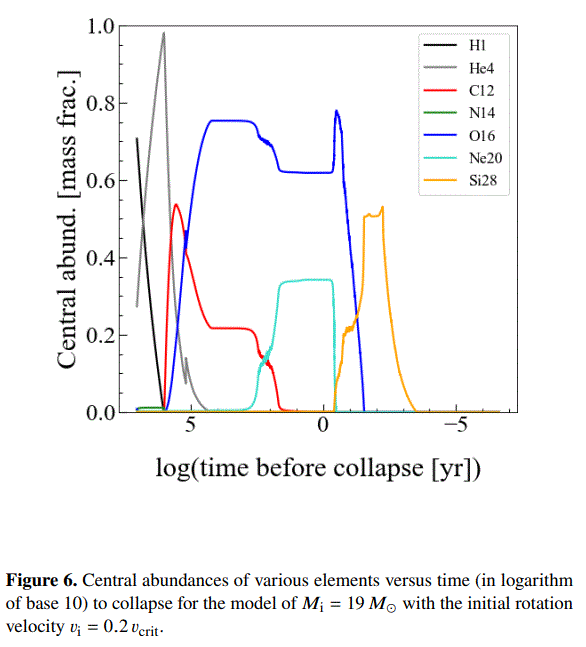
At the end of it’s life after a star runs out of hydrogen to fuse, it starts to collapse. The extra pressure and heat that generates kicks off fusion with the helium core which produces carbon. When the helium runs out the star shrinks again and pressurizes the carbon core, fusing carbon into bigger elements. But these stages are shorter and faster. Below is a graph of the timelines (with a log scale), and in Saio’s latest estimate Betelgeuse is already burning through the carbon core and has less than 20% of the carbon left, and maybe as low as 0.5%. The red line (the carbon) is theoretically bottoming out in less than 10 to 100 years.
The game is over when it fuses its way up to iron:
Charlie Martin:
If the star masses more than the Chandrasekhar limit, gravity causes the stellar material to continue fusing, producing elements farther and farther up to iron and nickel. Eventually, though, the core of the star is largely iron, and the fusion of iron takes more energy than it releases. At that point, the equilibrium of fusion heat and gravitational pressure is broken. The star collapses inward at 20% or more of the speed of light; the shockwave compresses the core until the atoms collapse; and the electrons meet the protons, converting them to neutrons and neutrinos and releasing immense amounts of energy — 100 “foe“, or about 1046 Joules.
We may not see the supernova, but from 6:40 minutes we can at least see Dr. Becky Smethurst get genuinely excited. She explains it well. Though what are the odds, a star 10 million years old reaching the end of days in the 21st century. OK, I’m skeptical…
Sometimes it’s nice to get away from politics.
Just how far is Betelgeuse?
To put in perspective how little we know, I typed in “how far is Betelgeuse” and discovered to my surprise, we don’t have much idea. Three years ago Betelgeuse was “discovered” to be much closer than we thought at 543 light years away. But in January this year it was found to be 724 light years from Earth, or at least between 613 and 881 light years away. Righto…
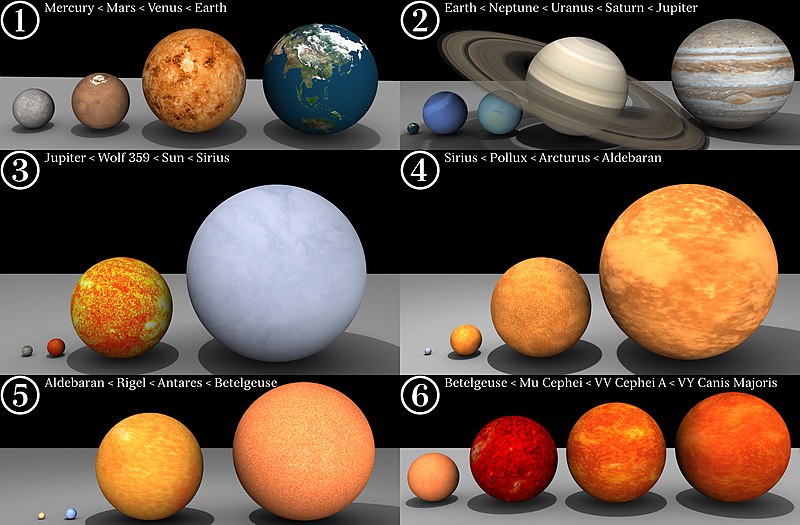
Betelgeuse is a biggie. See the progression of astronomical bodies up to Betelgeuse in set 5. If it were where our sun is, it would reach past the asteroid belt. Lucky it isn’t our sun.

Dave Jarvis (https://dave.autonoma.ca/)
REFERENCES
“The evolutionary stage of Betelgeuse inferred from its pulsation periods” by Saio et al.